“Telemedicine can solve the accessibility issue, virtual clinics can drive down the cost, Electronic Medical Records can improve the quality of information available to doctors and hence the quality of care, wearables can aid in faster diagnosis.”
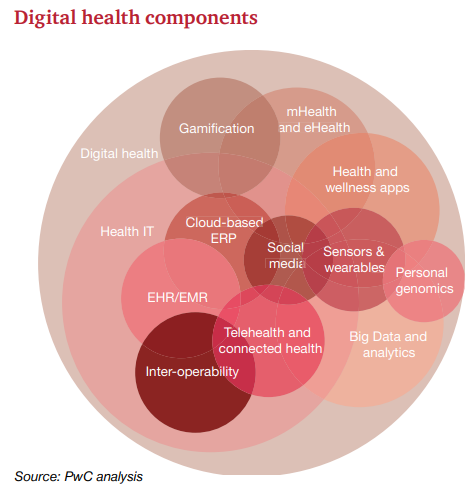
The National Digital Health Mission of the Government defines digital adaptation in healthcare as the creation of an ecosystem supporting universal coverage in an efficient, accessible, affordable, timely and safe manner, providing wide range of data, information and infrastructure services, leveraging open, interoperable, standards based digital systems, while ensuring the safety, confidentiality and privacy of health-related personal information. The above definition, with its wide breadth and critical nuances, provides some clue regarding the different aspects that digital adaptation needs to take care of in the case of healthcare, ranging from coverage, access, affordability to interoperability and data security.
“Many hospital and health care systems have employed chatbots and cameras, equipped with AI and ML algorithms to triage the patients based on probability of infection, severity of symptoms and other factors.”
Apart from all these challenges, the gains seem to be appropriately high too. Telemedicine can solve the accessibility issue, virtual clinics can drive down the cost, Electronic Medical Records can improve the quality of information available to doctors and hence the quality of care, wearables can aid in faster diagnosis.
A study found that considering the low proportion of Doctors in India (Doctor:Population ratio of 1:1456 against the WHO recommended 1:1000), digital solutions can free upto 15% medical professional time. The opportunities are truly endless from that aspect. forecast which hospitals and clinics would need emergency shipments of PPE kits and ventilators before the start of the new COVID-19 waves emergence and it could predict waves 2 weeks in advance with 85-90% accuracy based on patient generated data Triaging Covid-19 patients: Many hospital and health care systems have employed chatbots and cameras, equipped with AI and ML algorithms to triage the patients based on probability of infection, severity of symptoms and other factors. This has also helped in efficient allocation of scarce resources during the pandemic. Some notable examples are PSJH’s Grace chatbot, Partner’s Healthcare and Florida’s Tampa General.
Indian Hospitals
Apollo Hospitals: Has embraced Internet of Things (IoT) and digital technology for Telemedicine, disease management, real time patient tracking through ‘Patient Mantra’, a RTLS/RFID based solution for tracking movements of patients through a series of diagnostic procedures.
AIIMS: Simply by shifting to online registration, waiting times have been reduced. The AIIMS AVC clinic allows patients to have video consultations rather than in-person visits, making care more accessible.
Fortis: Using the hospital’s app, patients can obtain information on physicians and services provided by the Fortis Network, and can use the throughout the organization. Many health systems have senior executives holding the posts like Chief data Officer, Chief Digital Officer for this purpose. This not only legitimizes the leadership’s drive for digital adaptation, but also helps better planning and implementation.Cross industry hiring from the technology sectors can also help with implementation of better technology.

Roadmap/Checklist for the Digital Adaptation journey
Analyze the baseline: Evaluate what you already have and what is working well
Needs Assessment: Determine the issues, reasons for action, the desired state and the gap
Chart a roadmap: Chart out the detailed roadmap for adaptation by involving stakeholders from all levels including doctors, nurses, the Board and patients.
Experiment and implement: Conduct small scale experiments/trials to ensure adoption and resolve the complications and implement the refined solutions.
Ensure ongoing support for continuous improvement: Ensure the solutions suggested get actually adopted and become a core part of the hospital’s processes. Build a culture for continuous improvement, going through the above cycle.
Opportunities
Opportunities lie in the areas of Management (resource allocation, monitoring, process improvement), Security (data protection, replication, large scale secure storage), Legal and Administration. Whether it is Healthcare Information Systems, Medical Devices or platforms for Collaboration-Digital Adaptation can improve care delivery by leaps and bounds. Electronic Medical Records will provide real time up to date patient information, thus reducing the information asymmetry, medical devices like sensors, wearables, surgery robots, BioMed devices can help with the diagnosis and treatment, the information to choose and make appointments with the Doctors.
Manipal Hospitals: It’s mobile app not only manages payments, but also provides central access to medical reports and can help in tracking health vitality. Manipal Hospitals has also adopted IBM’s Watson to recognize patterns in images of human tissues for better diagnosing of cancer.
“Healthcare is first and foremost human. It is important to understand that healthcare is personal and even if a robot diagnoses a disease correctly, people might not be satisfied due to the lack of human touch.”
Challenges for Implementation
The above opportunities and use cases are not without their challenges. Below provides a brief discussion, aided by comments from leading Doctors and industry experts.
Data Security: Cyber security threats associated with electronic medical records can hamper digital adaptation. Health records fall in the category of Personal Identifiable Information; thus any leakage will result in grave consequences for the patients. The concern is all the more heightened due to the high value placed on medical data in dark web transactions.
Lack of Human Touch: Healthcare is first and foremost human. It is important to understand that healthcare is personal and even if a robot diagnoses a disease correctly, people might not be satisfied due to the lack of human touch. Another issue are the grave consequences in case of wrong diagnosis or errors in the process, unlike the manufacturing sector. technology platforms can help with collaboration through remote medical facilities, instant messaging, telemedicine and records sharing.
Exemplary Use-Cases during Covid-19
Using Cloud, AI & ML to predict Covid-19 waves: Providence St. Joseph Health, the 3rd largest health system in the US, entered into a strategic alliance with Microsoft, harnessing the power of Microsoft Azure and Artificial intelligence(AI) to transform patient-centric care. They used the native Machine learning (ML) and AI capabilities of Azure to analyze their data and Interoperability and lack of standards: Dr. Arpit Paliwal, Director of Happy Reliable Surgeries feels that lack of interoperability due to missing standards like DICOM for data production and sharing lead to issues of adoption.
Documentation: Dr. Arvind Kasargod of Cloudnine Hospitals suggests the need for better documentation, especially of outpatient clinics (the responsibility of documentation of outpatient clinics is that of patients) to facilitate digital health card and digitization initiatives.
Lack of incentives: Absence of stakeholder buy-in and adequate incentives for care providers to adopt digital solutions can lead to lower adoption of the technology. Even in cases of adoption, inadequate commitment can lead to issues and can hinder benefits. Hence, it is important to manage incentives, and ensure that decisions are taken while keeping the long-term vision in mind, rather than based on a transactional approach.
Other challenges: Issues of unclear and delayed returns on investment, huge upfront cost, scarcity of AI talent, complex stakeholder relationship management further complicate the above.
Talent Management to facilitate Digital Adaptation
It is important to have leadership buy-in, who can drive digital adaptation
“Agrawal Vishal Satish, Section B of HCOM course in IIM Lucknow is working under the guidance of Prof.S.Venkataramanaiah.”

