Ms. Mercilina Norman
“THE BODY ACHIEVES WHAT THE MIND BELIEVES”
In today’s fast-paced world, the intricate connection between physical and mental health has garnered significant attention. The phrase “strong body, strong mind” aptly encapsulates the holistic approach that underscores the profound interdependence between our physical state and mental well-being. This relationship is pivotal for maintaining overall health and resilience amidst the increasing stressors and sedentary lifestyles characteristic of modern life. Recognizing and nurturing this mind-body connection is more crucial than ever in our era of heightened health challenges.
Knowing this link helps us make wise lifestyle decisions, from the effects of regular exercise on mood and cognitive performance to the influence of mental health on physical resilience. Come explore the science underlying this symbiotic relationship with us, and learn how to bring about a healthy balance that supports general health and well being.

THE BIOLOGICAL BASIS OF THE MIND-BODY CONNECTION
The connection between physical and mental health is deeply embedded in our biological systems. Our body and mind are intertwined through complex biochemical pathways involving the nervous system, endocrine system, and immune system, which work in concert to maintain homeostasis and respond to various stimuli.
The Nervous System
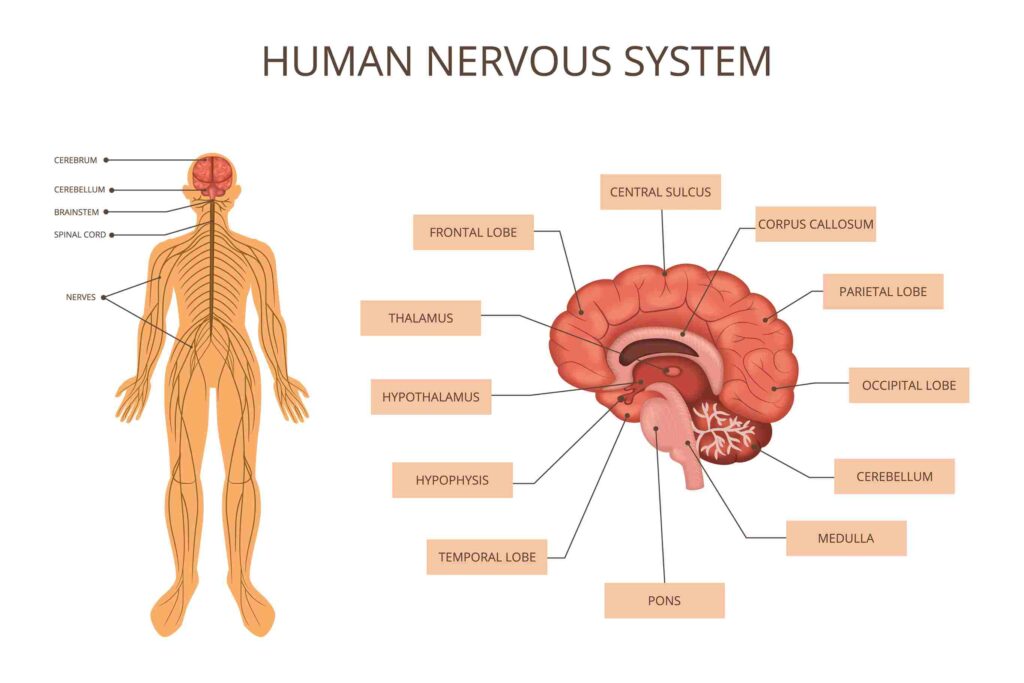
The nervous system, consisting of the central and peripheral systems, plays a fundamental role in linking physical and mental health. Neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and endorphins, which are crucial for mood regulation, also impact physical functions such as pain perception and energy levels. For instance, serotonin not only influences mood but also affects sleep patterns, appetite, and muscle function. Low levels of serotonin are commonly associated with depression and physical symptoms like fatigue and pain, illustrating the tight coupling between mental states and physical health.
Moreover, the autonomic nervous system, comprising the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches, regulates our body’s response to stress and relaxation. Chronic activation of the sympathetic nervous system due to prolonged stress can lead to a myriad of health issues, including hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic disorders. Conversely, activating the parasympathetic nervous system through relaxation techniques can promote recovery and healing, highlighting the bidirectional influence of mental and physical health.
The Endocrine System
The endocrine system, responsible for hormone production and regulation, significantly influences the interplay between physical and mental health. Stress triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone that prepares the body for a “fight or flight” response. While acute stress responses can be adaptive, chronic stress leads to sustained high cortisol levels, which can result in various health problems such as anxiety, depression, weight gain, and immune suppression.
Additionally, hormones like adrenaline and norepinephrine, which are part of the body’s immediate stress response, can have lasting effects on both mental and physical health. Chronic stress can also disrupt the balance of other hormones such as insulin and sex hormones, leading to conditions like diabetes and reproductive health issues. This complex interplay highlights the necessity of managing stress to maintain overall health.
The Immune System

The immune system’s interaction with stress and emotional states provides further evidence of the mind-body connection. Chronic stress and negative emotions can suppress immune function, increasing susceptibility to infections and illnesses. For example, stress-related hormones like cortisol can inhibit the production of cytokines, which are critical for immune responses. Over time, this immunosuppression can lead to a greater incidence of illnesses and slower recovery from infections.
Conversely, positive emotions and mental well-being are linked to stronger immune responses. Studies have shown that individuals with a positive outlook on life tend to have higher levels of antibodies and other immune markers, indicating a more robust immune function. This correlation underscores the importance of mental health for maintaining a strong immune system and overall physical health.
PHYSICAL HEALTH’S IMPACT ON MENTAL WELL-BEING
Exercise and Mental Health
Regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to enhance mental health. Exercise stimulates the release of endorphins, often referred to as “feel-good” chemicals, which can help reduce stress and elevate mood. Additionally, physical activity increases the production of neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, which are crucial for mood regulation and the prevention of conditions such as anxiety and depression.

Numerous studies have demonstrated the benefits of exercise for mental health. For instance, research published in the American Journal of Psychiatry found that regular physical activity significantly reduces the risk of developing depression, even among individuals with a genetic predisposition to the disorder. Exercise also promotes neurogenesis, the formation of new neurons, in areas of the brain associated with mood regulation, such as the hippocampus. This neurogenesis is thought to contribute to the antidepressant effects of exercise.
Furthermore, engaging in physical activities, especially in natural environments, has been shown to improve cognitive function, reduce symptoms of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and enhance overall psychological resilience. Activities like yoga and tai chi, which combine physical movement with mindfulness, are particularly beneficial for reducing anxiety and improving emotional well-being.
Nutrition and Mental Health

Diet plays a crucial role in influencing mental health. A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and omega-3 fatty acids supports brain function and mental health. For example, omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and nuts, are essential for cognitive function and have been shown to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. Antioxidants, found in fruits and vegetables, help protect brain cells from oxidative stress, which is linked to neurodegenerative diseases and cognitive decline.
Conversely, a diet high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats is associated with an increased risk of mental health problems. Research has linked poor dietary habits to mood disorders, cognitive decline, and other mental health issues. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Affective Disorders found that a diet high in sugar and refined carbohydrates is associated with an increased risk of depression and anxiety.
Moreover, certain nutrients, such as vitamin D and magnesium, play a critical role in brain health and mood regulation. Deficiencies in these nutrients have been linked to increased risk of depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline. Thus, maintaining a diet that provides adequate levels of essential nutrients is crucial for mental health.
Sleep and Mental Health
Adequate sleep is essential for both physical and mental health. Sleep supports physical restoration, memory consolidation, and emotional processing. Chronic sleep deprivation, on the other hand, is linked to a range of mental health issues, including depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline.
Studies have shown that individuals who do not get enough sleep are more likely to experience mood disorders and have a lower quality of life. For example, research published in the Journal of Psychiatric Research found that insomnia is a significant risk factor for the development of anxiety and depression. Sleep disturbances can also exacerbate symptoms of existing mental health conditions, creating a vicious cycle of sleep deprivation and worsening mental health.
Furthermore, poor sleep quality is associated with increased inflammation and stress hormone levels, which can contribute to physical health problems such as cardiovascular disease and metabolic disorders. Thus, prioritizing good sleep hygiene is crucial for maintaining both mental and physical health.
Chronic Illness and Mental Health
Chronic physical conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and chronic pain can significantly impact mental health. Managing the physical symptoms, limitations, and emotional stress associated with chronic illness often leads to increased rates of anxiety and depression.
For example, chronic pain not only affects physical well-being but also has a profound impact on mental health. Persistent pain can lead to feelings of helplessness, anxiety, and depression, as well as reduce overall quality of life. Additionally, the stress of managing a chronic condition can exacerbate symptoms of mental health issues, creating a complex interplay between physical and mental health.
Addressing the mental health needs of individuals with chronic illnesses is essential for improving their overall well-being and quality of life. This includes providing access to mental health services, support groups, and interventions that address both the physical and emotional aspects of chronic illness.
MENTAL HEALTH’S INFLUENCE ON PHYSICAL WELL-BEING
Stress and Its Physical Manifestations
Prolonged stress has a profound impact on both mental and physical health. Chronic exposure to stress hormones like cortisol can lead to various health issues, including hypertension, weakened immune function, and an increased risk of chronic conditions such as diabetes and heart disease.
For example, individuals experiencing chronic stress are more likely to develop cardiovascular problems due to the constant activation of the body’s stress response. This persistent state of heightened alertness can lead to elevated blood pressure, increased heart rate, and a higher risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Managing stress through techniques such as mindfulness, relaxation exercises, and lifestyle changes is crucial for maintaining both physical and mental well-being. Practices like deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and meditation can help activate the body’s relaxation response, reducing stress hormone levels and promoting healing.
Depression and Physical Health
Depression impacts physical health in numerous ways, including fatigue, headaches, and digestive problems. There is also a strong link between depression and an increased risk of chronic illnesses such as diabetes and heart disease.
Individuals with depression are more likely to engage in unhealthy behaviors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and substance abuse, which can further deteriorate physical health. Moreover, the physiological changes associated with depression, such as increased inflammation and altered hormone levels, can contribute to the development of chronic diseases.

Effective treatment of depression, including therapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications, can lead to improved outcomes for both mental and physical health. Addressing the underlying mental health issues is essential for breaking the cycle of poor health behaviors and improving overall well-being.
Anxiety and Physical Health
Anxiety disorders are associated with various physical symptoms, including headaches, muscle tension, and digestive issues. Chronic anxiety is also linked to a higher risk of developing conditions such as heart disease and hypertension.
For instance, individuals with chronic anxiety often experience increased muscle tension and physical discomfort, which can lead to chronic pain and other health problems over time. The constant state of heightened arousal associated with anxiety can also contribute to the development of cardiovascular issues, such as elevated blood pressure and increased heart rate.
Addressing anxiety through therapeutic interventions, medication, and lifestyle changes can help improve overall well-being and reduce the risk of associated physical health problems. Techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), mindfulness meditation, and regular physical activity have been shown to be effective in managing anxiety and improving physical health outcomes.
Psychosomatic Conditions
Psychosomatic conditions refer to physical symptoms that are influenced or exacerbated by psychological factors. Examples include tension headaches, chronic pain, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), which are often associated with emotional stress and mental health issues.
Managing psychosomatic conditions requires a holistic approach that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of the condition. Integrating mental health services with physical health care can lead to better outcomes for individuals with psychosomatic disorders. Techniques such as stress management, psychotherapy, and lifestyle modifications can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
THE ROLE OF HOLISTIC AND INTEGRATIVE HEALTH APPROACHES
Holistic Health

Holistic health approaches consider all aspects of health, including the physical, emotional, mental, and spiritual components. These approaches aim to address the root causes of health issues rather than just treating symptoms, promoting overall health and balance.
Holistic practices such as acupuncture, massage, and nutritional counseling have been shown to improve both physical and emotional well-being. For instance, acupuncture has been demonstrated to reduce physical pain and alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression. Similarly, massage therapy can help reduce stress, relieve muscle tension, and promote relaxation.
Moreover, holistic health approaches often incorporate lifestyle changes and self-care practices, such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and stress management, which support overall well-being. By addressing the underlying factors that contribute to health problems, holistic approaches can lead to more sustainable and effective health outcomes.
Integrative Medicine

Integrative medicine combines conventional and alternative medical treatments to provide a comprehensive approach to healthcare. This approach recognizes the importance of addressing both physical and mental health needs to achieve optimal well-being.
Integrative medicine techniques may include combining conventional medical treatments, such as medication and surgery, with alternative therapies like mindfulness meditation, yoga, and dietary adjustments. For example, a patient with chronic pain might benefit from both physical therapy and acupuncture, as well as mindfulness practices to manage stress and emotional responses to pain.
By treating the whole person and integrating various treatment modalities, integrative medicine aims to promote overall health and well-being. This approach encourages collaboration among healthcare providers and empowers patients to take an active role in their health and wellness.
Mind-Body Practices
Mind-body practices such as yoga, tai-chi, and mindfulness meditation have gained popularity for their benefits in enhancing both mental and physical well-being. These practices help reduce stress, improve mood, and increase physical fitness.
For example, research has shown that mindfulness meditation can reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, as well as improve physical health outcomes such as blood pressure and immune function. Similarly, yoga and tai chi have been shown to improve flexibility, strength, and balance, as well as reduce stress and promote relaxation.
Incorporating mind-body practices into daily life can help strengthen the connection between the mind and body, supporting overall health and well-being. These practices encourage self-awareness, emotional regulation, and physical activity, which are essential components of a holistic approach to health.
PRACTICAL TIPS FOR INTEGRATING PHYSICAL AND MENTAL HEALTH

- Exercise Regularly: Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking, running, cycling, or strength training, to boost both physical fitness and mental well-being. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week. Exercise not only improves physical health but also releases endorphins that enhance mood and reduce stress.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats to support brain function and overall health. Avoid excessive consumption of processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats, which can negatively impact both physical and mental health. Incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods can help improve mood, cognitive function, and energy levels.
- Prioritize Sleep: Ensure you get enough quality sleep each night to support both physical and mental health. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night and establish a regular sleep routine. Good sleep hygiene, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a restful sleep environment, is crucial for overall well-being.
- Practice Mindfulness and Relaxation: Incorporate mindfulness practices, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, into your daily routine to reduce stress and promote mental clarity. Regular practice of mindfulness can help improve emotional regulation, reduce anxiety, and enhance overall well-being.
- Stay Connected: Maintain strong social connections with friends and family to support emotional well-being and reduce feelings of isolation and loneliness. Social support is essential for mental health and can help buffer against stress and adversity.
- Seek Professional Help: If you are struggling with mental health issues, such as depression or anxiety, seek professional help from a therapist or counselor. Addressing mental health needs is crucial for overall well-being and can help improve both mental and physical health outcomes.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress management techniques, such as yoga, tai chi, or journaling, to help reduce stress and improve both physical and mental health. Developing healthy coping strategies for managing stress can enhance resilience and overall quality of life.
- Engage in Activities You Enjoy: Participate in activities and hobbies that bring you joy and fulfillment to enhance your mental well-being and overall quality of life. Pursuing interests and passions can provide a sense of purpose and satisfaction, contributing to overall happiness and well-being.
The interconnection of physical and mental health highlights the importance of adopting a holistic approach to well-being. By recognizing and nurturing the mind-body connection, we can achieve a balanced and fulfilling life. Maintaining a strong body through regular exercise, proper nutrition, and adequate sleep, combined with practices that support mental health, such as mindfulness and stress management, is essential for overall well-being. Embracing a holistic approach to health allows us to live healthier, happier, and more resilient lives, ultimately leading to a stronger body and a stronger mind.The relationship between physical and mental health is a complex and dynamic one, with each influencing and supporting the other. By taking a comprehensive approach to health that addresses both physical and mental needs, we can achieve optimal well-being and improve our quality of life. Whether through exercise, nutrition, sleep, or stress management, integrating physical and mental health practices into our daily lives is key to living a balanced and fulfilling life.
Author’s Biography
Mercilina Norman is currently pursuing an MBA in Healthcare and Hospital Administration at Jamia Hamdard University, New Delhi. She holds a BSc in Nursing from Chaudhary Charan Singh University,Meerut. With experience as a Registered Staff Nurse at Max Healthcare,Saket,Mercilina excels in advanced cardiac care and patient satisfaction.